Make Big Challenges Small using OO .NET Transaction Construct & SQL
- Mission Critical / Industrial Strength Power and Scalability
- for those SQL update processes active for multiple users and requiring the highest level of accuracy and concurrency
- simplifies multi-user considerations
- our proactive approach usually beats out alternatives such as backing into a
solution involving isolation levels and process timing
- Access MS SQL Server or IBM Db2 for i or Other DBs*
- from c# (or VB.NET or 3rd Party) Languages in Code-Behind in conjunction with the .NET OO Framework
- Solve intermittent problems such as inconsistent run times in SQL processes
- Could row locking decisions made behind the scenes by your database management software be the culprit?
- proactively control which records are locked and which can be read by other update processes is best
- reactive after-the-build strategies that try to fix multi-user or concurrency software design deficiencies are rarely, if ever,
perfect and aren't the way to go, plus you'll still need expert support resources
- Let us tell you about this technique to help you get into tune with these facets.
- Nail down row locking with our technique and gain these benefits
- drastically reduce rollback situations or wait times (when updates to 2nd or 3rd file in line cannot be completed) (pessimistic row locking)
- eliminate ability or need for other transactions to read uncommitted data or interim transaction results (dirty reads) and vice-versa
- Technique does not Preclude Use of DB Constraints & Rules
- but in some cases detecting lock conditions that would cause roll-back midstream
- use when a two-phase or two-pass approach is needed
- use in high volume situations where overlays are occurring
- use for types of updates where frequent rollback is costly and/or inefficient
- simplify concurrency considerations. This technique:
- uses optimistic row locking to prevent overlays even at the column level (goes beyond techniques using the record level timestamp for example)
- uses pessimstic row locking to explicitly lock rows (from other update processes) in multiple files between initial access and actual update
- Boom!, you've got something super solid...
- Solve classic problems in a straight-forward manner
- when inventory levels or detection of stock-out conditions need to be real time accurate
- inventory quantity allocation at order entry time
- pick/pack sheet print
- when it is costly to POS sell more than you have
- processes involving large numbers of order line updates and order header status changes
- next unique invoice number assignment
- Technique
- Note: Use of this transaction technique from c#, VB.NET or Visual RPG for .NET allows commit and rollback boundaries to span across multiple stored procedure calls and SQL statements
- Connect
- Start Transaction
- MS SQL Server Database Example:
-
using System.Data.SqlClient;
System.Data.SqlClient.SqlTransaction sqltxEnvironmentMasterRowUpdate = null; -
sqltxEnvironmentMasterRowUpdate = cnnsvcMSSQL.BeginTransaction();
- Db2 for i Database Example:
-
using IBM.Data.DB2.iSeries;
-
IBM.Data.DB2.iSeries.iDB2Transaction sqltxDigitalAssetDeliveryUIEventRowUpdate = null;
-
sqltxDigitalAssetDeliveryUIEventRowUpdate = cnnsvcDB2iSQL.BeginTransaction();
- Prevent Interim Result Overlays - Access Data & Hold Pessimistic Row Lock(s)
- Verify No Data Overlay Conditions (otherwise message user and rollback)
- Start Update(s)
- Commit if Successful, Otherwise Rollback
- Dispose and Disconnect
- Demonstrating the Technique in a Master File Data Layer
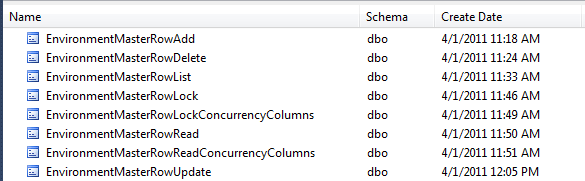
- Basically, all data access, update and inquiry processes are encapsulated into 8 stored procedures for each master file
- Equivalent function in the data layer in both SQL Server and Db2 for i
- The techniques explained here are fully implemented
- This MSSQL set of of stored
procedures is in use at
EnvironmentMasterInquiry.aspx.
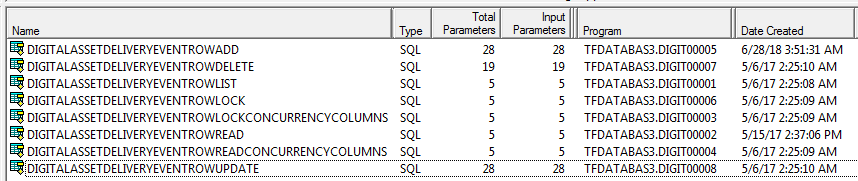
- Here is a list of SQL PL
stored procedures on Db2 for i (in use at DigitalAssetDeliveryEventInquiry.aspx).
|


|